The Role of Vitamins D in Eye Health is multifaceted, influencing various aspects of ocular function. The blood vessels supplying the eyes are tiny and can easily become blocked. The foods we eat can play a significant role in our eye health. Just like the other body organs, your eyes need the right nutrients to function best. Foods rich in essential vitamins and minerals can help protect our vision and protect our eyes from diseases.
Luckily, essential vitamins for eye health are easy to find in our daily diet. A healthy diet leads to healthy eyes; an unhealthy diet leads to unhealthy eyes. But “healthy eating” is a very vague concept. So bad foods for eye health tend to fall into some extensive categories. Your eyes need a variety of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to function properly. These nutrients help protect your eyes from damage, improve blood flow, and support overall eye health.
Vitamin D:-
Vitamin D, often called the “sunshine vitamin” because our bodies make it when exposed to sunlight, does more than just keep our bones strong. It might also play an important role in eye health. Vitamin D seems to have many ways of supporting eye health. It can help reduce inflammation in the eyes, which can be a problem in conditions like dry eye. It also helps protect the front part of your eye and may even improve tear production. Some studies even suggest that using vitamin D drops or eye ointments might help heal the surface of the eye.
Vitamin D and Eye Conditions:
The role of Vitamin D in eyes health play vital role, the effects of vitamin D are well known and apply to the ocular surface immune cells and structural cells. The role of vitamin D in ocular surface conditions such as dry eye disease (DED), and chronic inflammation in the eyes can cause conditions like dry eye syndrome. Vitamin D may help regulate the production of tears by reducing inflammation, which is essential for keeping your eyes moist and comfortable. Keratoconus (KC) is a disorder of the eye that results in progressive thinning of the cornea. The protrusion of the cornea may result in blurry vision or double vision. Age-related macular Degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults. Diabetic Retinopathy affects people with diabetes and can damage the blood vessels in the back of the eye. Low vitamin D levels in premature babies have been linked to an increased risk of eye problems.
Best sources of vitamin D:-
There are two sources of vitamin D available to humans: dietary sources and local synthesis in the skin.
Sun synthesis:-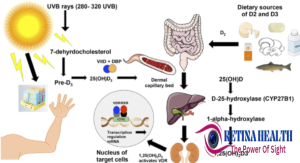
Sun exposure is the most important natural source of vitamin D. The body uses the vitamin to absorb the calcium it needs to build and maintain bones. Extrarenal synthesis has been demonstrated in many tissues including the skin, respiratory system, breast, colon, endometrium, and prostate. Similarly, the eye has many cell types including corneal epithelial cells, endothelial cells, scleral fibroblasts, and retinal pigment epithelial cells. Getting adequate sunlight is the best way to help the body produce enough vitamin D. Experts suggest getting 10-30 minutes per day, several times a week to maintain healthy blood levels. This time may fluctuate depending on how sensitive your skin is to sunlight. The sun is our best natural source of vitamin D. Spending even a short time in the sun can provide the body with all of the vitamin D it needs for the day. Many factors affect how much vitamin D a person gets from the sun, such as:
- Time of day. The skin produces more vitamin D when in the sun during the middle of the day, the time it is at its highest point in the sky. When spending prolonged time in the hot sun, wear sunscreen, and stay hydrated.
- Amount of skin exposed. The more skin a person exposes, the more vitamin D the body will make. Exposing the back, for instance, allows the body to produce more vitamin D than just the hands and face.
- Skin color. Pale color skin makes vitamin D more quickly than darker-colored skin.
- light skin: 15 minutes for a person with light skin
- dark skin: a couple of hours for a person with dark skin
People can ensure they get enough of the vitamin by scheduling regular time outdoors. When the sun’s ultraviolet rays hit a person’s skin, processes inside the tissue start making vitamin D for the body to use.
Dietary sources:-
Some foods are higher in vitamin D than others. Certain foods can also be good sources of vitamin D such as:
- Fish: fatty fish, such as salmon, sardines, mackerel, and tuna
- Nuts and seeds: almonds, Brazil nuts, pumpkin seeds and sesame seeds
- Fruits and vegetables: avocado, mushrooms, dark leafy vegetables such as spinach and collard greens
- Breakfast cereal
- Egg yolks
- Beef liver
- Dairy: cheese, fortified milk, yogurt
- Fortified cereals and juices
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency:-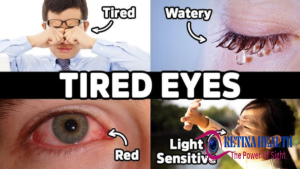
The role of Vitamin D in eyes play an important role ,being deficient in Vitamin D can also hurt eye health. A vitamin D deficiency may produce no symptoms, or symptoms may take several years to appear. However, it may increase the risk of long-term health problems.
- Regular sickness or infection
- Eye problem
- Fatigue
- Bone pain
- Osteoporosis, Muscle weakness, muscle aches or cramps
- Low mood
- Hair loss
- dental problems
How much is a deficiency?
The results of a serum vitamin D blood test shown by trusted resources are the following:
- Too high and possibly harmful: 125 nmol/l or more
- Sufficient: 50–125 nmol/l
- At risk of inadequacy: 30–49 nmol/l
- At risk of deficiency: 30 nmol/l or less
Causes of a deficiency:-
Vitamin D deficiency in eyes can happen when there is insufficient vitamin D in the body. Its deficiency is a global problem affecting an estimated 1 billion individuals. It also hurts eye health. Many influencing causes may lead to lower vitamin D levels if a person:
- does not consume enough vitamin D
- is unable to absorb or metabolize the vitamin D
- does not spend enough time in ultraviolet (UVB) sunlight
Risk factors for vitamin D:-
Various factors can increase the risk of a deficiency.
- Age, Individuals over the age of 65 years
- Insufficient sunlight exposure
- Being overweight or obese
- A diet lacking fish or dairy
- Medication use that alters vitamin D metabolism
- Lifestyle factors
- Geographical factors
- Breastfeeding infants
- Skin type
- Smoking
- Pollution:
Prevention and treatment:-
The majority of middle-aged adults are at increased risk of vitamin D deficiency due to decreased sun exposure and increased use of sunscreens. Therefore, studies show that to reach a serum level of 25 (OH) D above 30 ng/ml a minimum of 1000 IU or probably 1500-2000 IU/day is necessary: The best way to prevent a vitamin D deficiency is to eat foods that are rich in this nutrient and to spend some time outside each day. The treatment of vitamin D Insufficiency/deficiency except in rickets and osteomalacia and without hypocalcemia. Some tips for avoiding a deficiency include:
- Maintaining a healthy body weight: Cycling or walking can provide both exercise and exposure to sunlight.
- Maintenance treatment: People with health conditions that affect the absorption of nutrients may find that treating the underlying condition helps boost their levels of certain nutrients, including vitamin D.
- Being proactive about preventive health: Replenishing vitamin D stores more than 30 ng/ml, People with a family history of osteoporosis or vitamin D deficiency may wish to consider speaking to their doctor about screening.
Sun exposure is the most important natural source of vitamin D. The body uses the vitamin to absorb the calcium it needs to build and maintain bones. Getting enough vitamin D is crucial to maintaining healthy bones. The easiest way of getting enough vitamin D is to regularly spend time outside, making sure that the arms, face, and legs have exposure. Short bursts of sun exposure can usually allow your body to produce all the vitamin D it needs for the day. Some people, including older people or those with kidney or liver problems, may be at risk of becoming deficient in vitamin D. They can consider eating more foods that contain vitamin D or taking a supplement. Depending on a person’s dietary preferences, consuming enough vitamin D may be difficult. In this case, vitamin D supplements, which are available to purchase online, may be a beneficial choice for exposing the skin to the sun. It is essential to consider the risk of skin cancer. People should avoid allowing their skin to burn.


